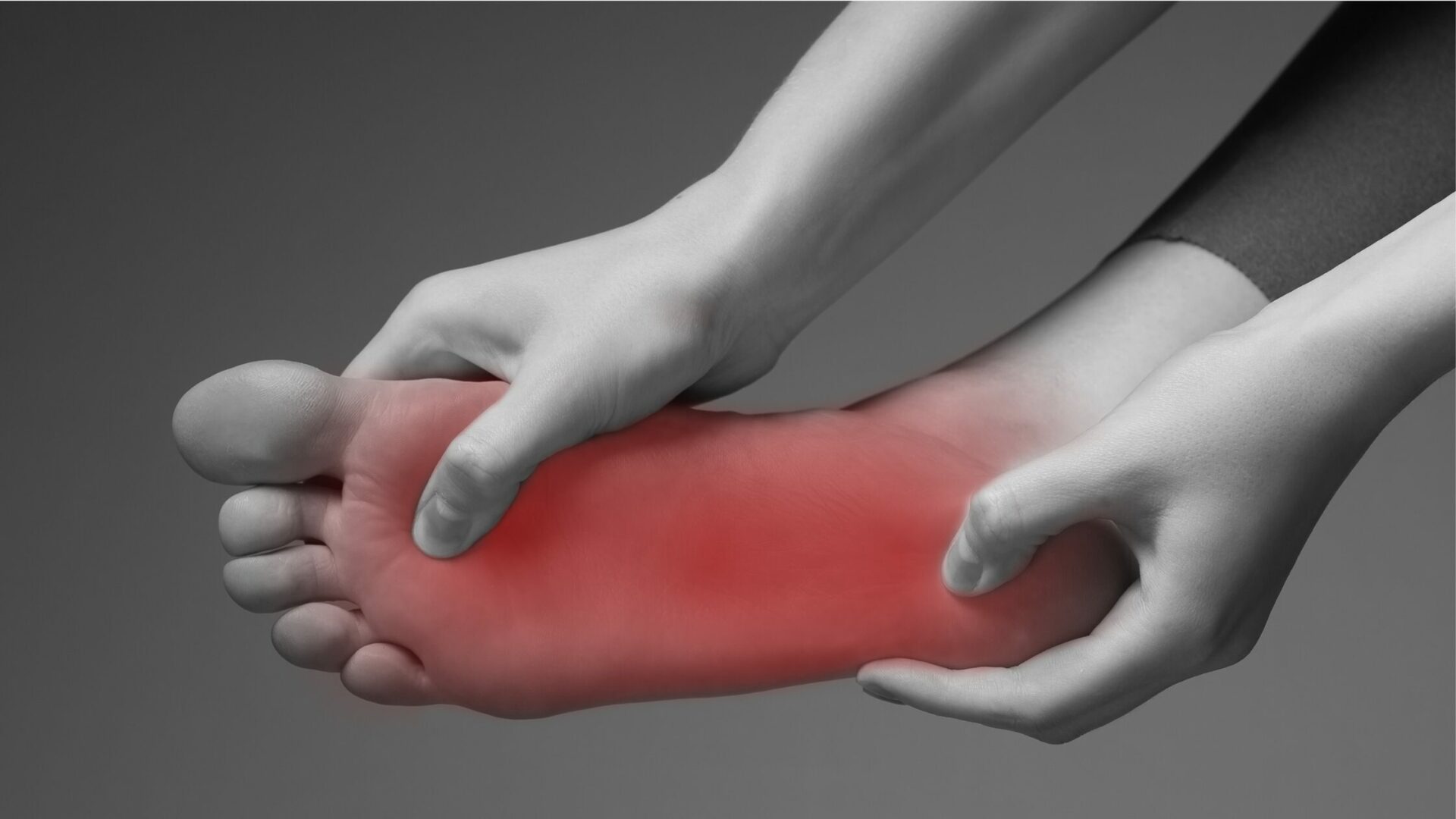
Diabetic foot problems happen because diabetes hurts the nerves and blood vessels in the feet. This hurts the feeling in the feet, called neuropathy. High sugar levels in the blood cause this. It makes the feet feel numb, tingly, or painful. This makes it easy to get sores on the feet, which can become ulcers or infections. Taking good care of your feet early on can help prevent these problems.
Table of Contents
Understanding Diabetic Foot Complications and Their Impact
Diabetic foot problems pose a significant threat to foot health, affecting millions globally. It is a common complication of diabetes. It causes numbness, tingling, and sharp pain. These increase the risk of foot ulcers and infections. Poor circulation, Charcot foot, gangrene, and amputation make foot issues worse. They show the need for proactive foot care and timely medical help.
Basic Diabetic Foot Complications
Diabetic foot complications include many issues. These issues include peripheral neuropathy and foot ulcers. They also include Charcot foot, gangrene, poor circulation, amputation, calluses, and skin changes. Each complication presents unique challenges, highlighting the necessity for comprehensive foot care strategies.
1. Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is caused by nerve damage. It is one of the most common diabetes complications. High blood sugar harms the nerves. It affects the feet and lower legs. The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy can vary from mild to severe and may encompass:
- Numbness or diminished ability to perceive pain or changes in temperature
- Tingling or burning sensations
- Sharp pains or muscle cramps
- Heightened sensitivity to touch
- Decreased reflexes, particularly noticeable in the ankles
- Impaired balance and coordination
Neuropathy often leads to foot deformities, ulcers, and infections. In severe cases, it requires amputation. So, keeping up foot care and controlling blood sugar are key. They stave off this complication.
2. Foot Ulcers
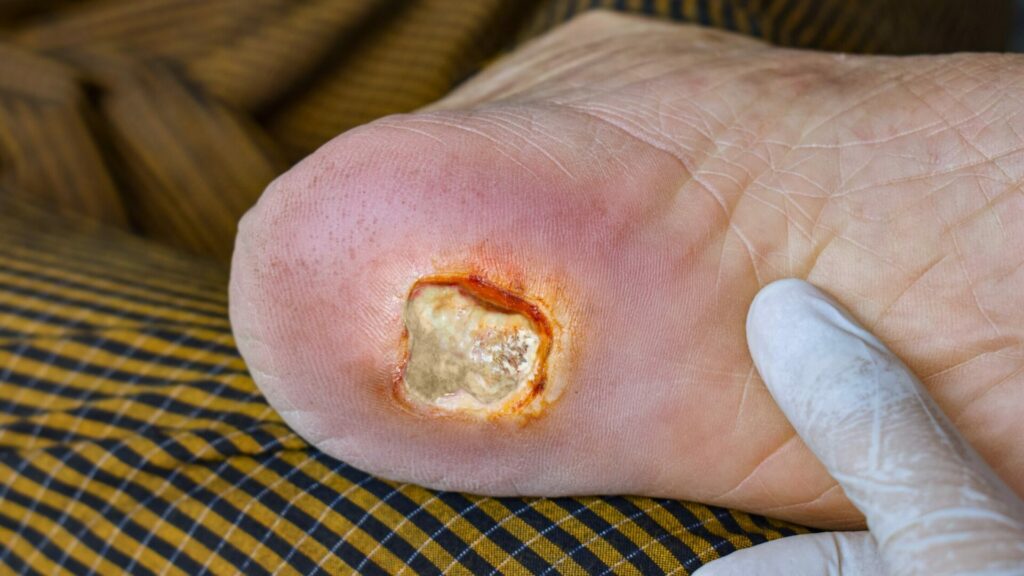
Foot ulcers are common among people with diabetes. They are open sores that do not heal or often come back. They tend to appear on the ball of the foot or the underside of the big toe. But they may also emerge on the foot’s sides.
These ulcers often come from small scrapes or cuts. They go unnoticed due to neuropathy or the pressure from fitted shoes. If neglected, these foot ulcers can grow. They can get infected and pave the way for more severe complications, like gangrene. In the end, they may require amputation.
3. Charcot Foot
Charcot foot is a serious condition. It affects people with severe neuropathy. In this condition, the foot bones weaken. This makes them prone to fractures or dislocations from minor stress or trauma. Peripheral neuropathy makes the problem worse. It causes people to keep walking on the injured foot. This makes the injury worse. So, the foot tends to deform, often assuming a distinctive ‘rocker-bottom’ appearance.
Swift intervention is imperative to facilitate foot healing and stave off further complications. Usually, treatment involves immobilizing the foot and ankle. This lasts for weeks or months. It allows inflammation to go down and bones to heal.
4. Gangrene
Gangrene happens when body tissues die from poor blood flow. This can come from an infection. Or from chronic diseases like diabetes. People with diabetes often have numbness in their feet. This makes them less sensitive to wounds or ailments. These issues could lead to gangrene.
Addressing this condition usually requires surgery to remove the dead tissue. In severe cases, it may require cutting off the affected limb. This shows the critical importance of consistent foot care. It also stresses the need for prompt medical help for injuries or infections.
5. Poor Circulation
In diabetes, poor circulation is a common complication. It greatly affects health, especially the feet. High blood sugar harms nerves and blood vessels. It reduces blood flow to the legs. This circulation problem hampers healing. It makes wounds, ulcers, or infections harder to manage. What may seem minor to people without diabetes can become a big issue for those with the condition.
Signs of poor circulation include cold feet, numbness, and tingling. Also, slow wound healing and skin color changes. Regular exercise, foot care, and a healthy lifestyle can improve circulation. They can also prevent problems. They play pivotal roles.
6. Amputation
Unfortunately, advanced diabetic foot disease can result in severe outcomes, such as amputation. Amputation can worsen conditions like digestive and kidney diseases. Diabetes causes peripheral neuropathy. This reduces feeling in the feet, making small injuries undetectable.
These unnoticed injuries can get worse. They can cause infections or even gangrene. This happens when they combine with poor circulation, which hinders healing.
If these conditions worsen and jeopardize the patient’s well-being, the doctor may need to amputate the foot or part of the leg. Nevertheless, the majority of amputations are preventable through diligent care and routine check-ups.
7. Calluses
Calluses manifest as thickened patches of skin resulting from recurring pressure or friction. Although they can develop in anyone, people with diabetes face a higher risk. This is due to peripheral neuropathy, which may cause uneven weight on the feet. This uneven weight prompts the formation of calluses.
Inadequately managed calluses can deteriorate and evolve into ulcers, characterized by open sores. So, it is key to not try to remove calluses or corns alone. Instead, give this task to a healthcare professional. They can evaluate and treat your feet carefully. This will prevent harm to your skin.
8. Skin Changes
Skin changes represent another prevalent issue for individuals living with diabetes. The skin on the feet may become dry and crack. This raises the risk of infection. Additionally, diabetes can induce alterations in foot coloration and temperature.
Also, high blood sugar can harm skin cells and nerves. This harm can cause various skin conditions. For example, it can cause diabetic dermopathy. Round, brown, or purple scaly patches mark this condition. High blood sugar can also cause digital sclerosis. This condition makes the back of the hands have tight, thick, waxy skin. It also affects the toes and forehead.
To reduce the risk of severe skin problems, you should adopt routines. These include regular moisturizing, gentle cleansing, and daily foot checks. If you notice any skin changes, ask a healthcare professional right away. They will assess and treat the problem.
Advanced Prevention Strategies from Diabetic Foot Complications
1. Controlling Blood Sugar Levels
Effective blood sugar management is crucial to preventing diabetic foot complications. Balanced blood sugar levels are key. You can keep them by eating, exercising, taking medicine, and reducing stress. You should also get check-ups. This can reduce the risk of diabetes and help keep your feet healthy.
2. Regular Foot Examination
Regular foot checks are key. You should do them yourself, and doctors should do them. They help find diabetic foot problems early. Vigilant monitoring allows for quick action. It reduces the chance of severe problems like ulcers and infections.
3. Maintaining Good Foot Hygiene
Proper foot hygiene is key. It includes daily washing and drying. It helps stop infections. They can make diabetic foot problems worse. Moisturizing dry skin helps. Trimming nails carefully does too. Both help foot health.
4. Wearing Proper Footwear
Choosing appropriate footwear is critical for individuals with diabetes. Good shoes fit well and support the feet. They prevent friction and pressure injuries. This reduces the risk of foot ulcers and other problems. Inspecting shoes for signs of wear and tear is also recommended.
5. Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity improves circulation. It helps control blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of diabetic foot complications. Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling are particularly beneficial for foot health.
6. Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers help find foot issues early. They also allow for quick intervention. Regular foot exams, vascular assessments, and neurological evaluations can cause complications. They discover them before they get worse. This allows for timely preventive measures.
Natural Supplements for Diabetic Foot Care
Managing diabetic foot complications involves many things. These include proper foot hygiene, regular check-ups, and lifestyle changes.
In addition to these measures, some natural supplements can help. They can use traditional treatments. They can also promote foot health in people with diabetes.
FAQ
What are signs of diabetic foot?
- Feeling tingling, burning, or pain in your feet.
- Noticing a loss of sensation or feeling heat and cold less.
- Seeing changes in the shape of your feet as time goes on.
- Observing a loss of hair on your toes, feet, and lower legs.
What is the treatment for diabetic foot?
Managing diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) involves several key steps. These include cleaning the wound surgically, using dressings to keep it moist and control fluids, offloading pressure from the wound, checking blood flow, and controlling infections and blood sugar levels. It’s best to coordinate these efforts through a team at a specialized clinic that focuses on diabetic foot wounds.
What happens to your feet if you have diabetes?
Lots of folks with diabetes have peripheral artery disease (PAD). This cuts down on blood flow to the feet. Plus, many also have neuropathy, which makes it hard to feel their feet. These two problems combined make it more likely to get ulcers and infections, possibly leading to amputation.
Is diabetic foot serious?
Diabetic foot problems can cause severe infections. If an infection starts, it might spread and hurt other areas like the legs. In serious cases, a doctor might suggest amputation to stop the infection and prevent more damage. Amputation means cutting off a part of the body, like a toe, foot, or part of the leg. Diabetes is one of the main reasons why people need amputations.
Conclusion
By adopting a comprehensive approach to foot care, individuals can effectively prevent diabetic foot complications and maintain optimal foot health, thereby enhancing their overall quality of life.